

Example 1 – Triangle:ĭraw a triangle on the whiteboard and highlight that a triangle is a 2-dimensional figure that has 3 sides that may or may not be equal. Then, provide examples of polygons and their properties. Ask students to circle the ones that are polygons and explain why these qualify as polygons. Also, polygons are always closed shapes – if the figure is open, it does not represent a polygon.ĭraw a few figures on the whiteboard, and make sure to include shapes that are polygons and shapes that aren’t. So polygon means ‘many angles’, and this refers to the angles formed by the straight lines (or sides) of the polygon.Īdd that a polygon always has straight sides – if the figure has one side that has a curve, it does not represent a polygon. Point out that in Greek, ‘poly’ means ‘many’, whereas ‘gon’ means ‘angle’. Thus, we have triangles, squares, rectangles, etc.Īsk students to reflect on the word polygon. It’s a 2-dimensional figure whose name is based on the number of its sides. Explain that a polygon is a closed plane figure, formed by connecting segments that are called ‘sides’. These properties make each 2-dimensional figure special, while there are also some that share common characteristics.Īdd that one example of 2-D figures are polygons. Point out that there are many 2-dimensional figures around us and that each of them has its own unique properties. If students understand the difference between 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional shapes, they should be able to recognize that the cylinder and rectangular prism have height in addition to length and width, and are not flat, hence they’re not 2-dimensional objects. While 2-dimensional shapes are flat figures with length and width, 3-dimensional shapes are solid figures with length, width, and height.ĭraw an example on the whiteboard where there are both 2-dimensional figures and 3-dimensional figures and ask students to circle the 2-dimensional ones. You can draw a distinction between the two to make things clearer. Students have also encountered 3-dimensional shapes.
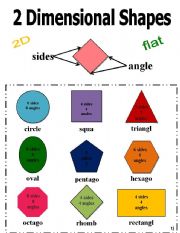
You can include shapes such as the following: If you have manipulatives or images, even better. Add that there are many different 2-dimensional shapes and draw examples of such shapes on the whiteboard. It is a flat plane figure that has no depth or thickness.īy now, students have come across many 2-dimensional shapes. Explain that a 2-dimensional shape (or a 2-D shape) is a shape that only has two measurable dimensions – length and width. Ideas for Teaching 2-Dimensional Shapes and Their Properties What Are 2-Dimensional Shapes?įor starters, define what 2-dimensional shapes are. Use them in your class and see students’ math knowledge soar in no time! Lessons on 2-dimensional shapes can be lots of fun if math teachers are equipped with the right resources! To this end, we bring you a few teaching ideas and awesome activities on this topic.
#TWO DIMENSIONAL SHAPES THAT HAVE 8 ANGLES HOW TO#
They gain an in-depth understanding of what these shapes represent, and learn how to identify their properties. In grade 5, students learn about the different 2-dimensional shapes, such as circles, squares, triangles, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
